

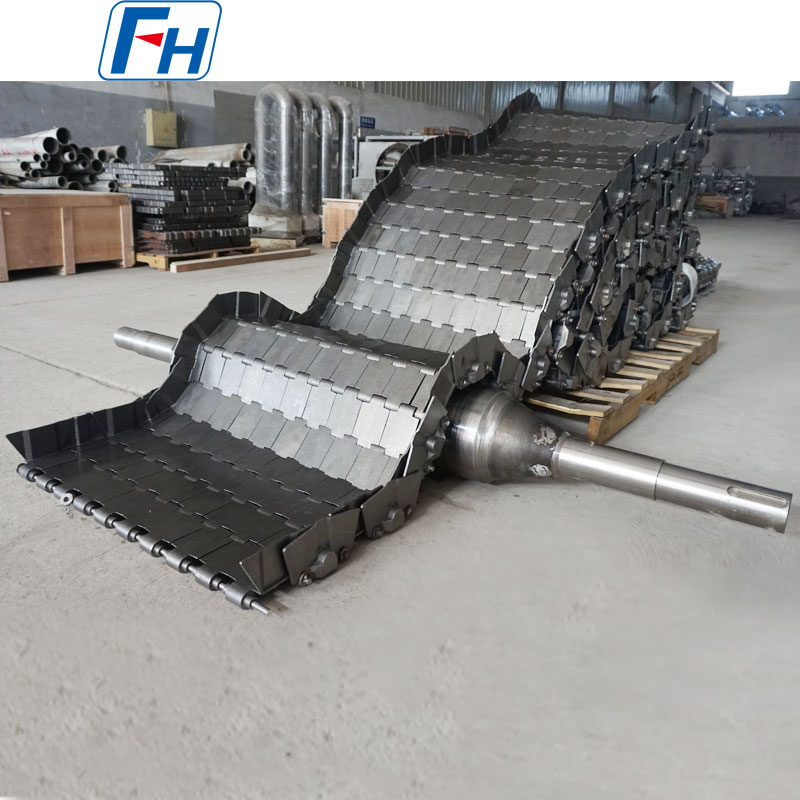
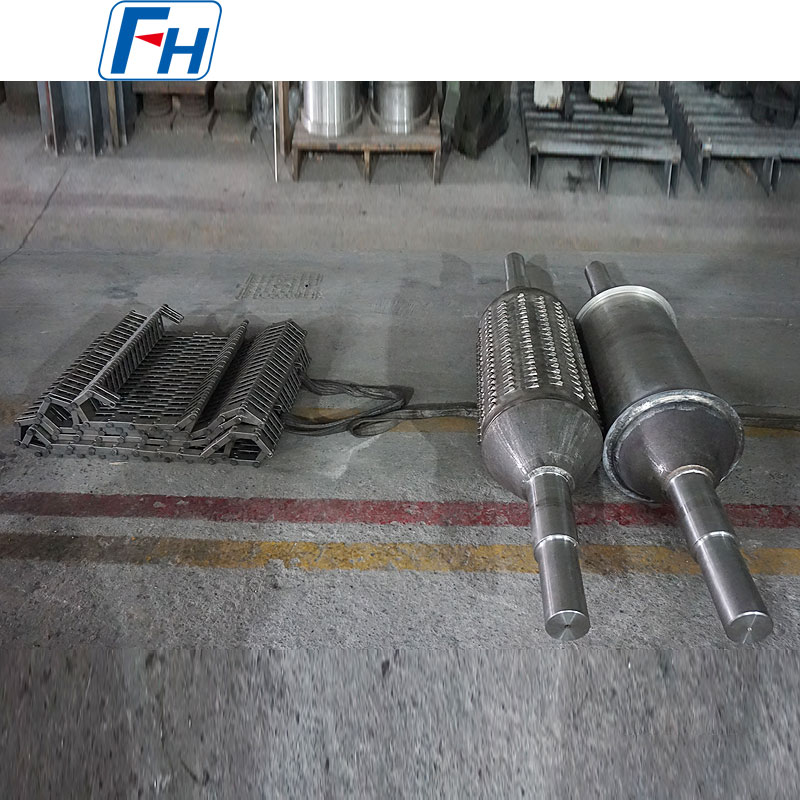
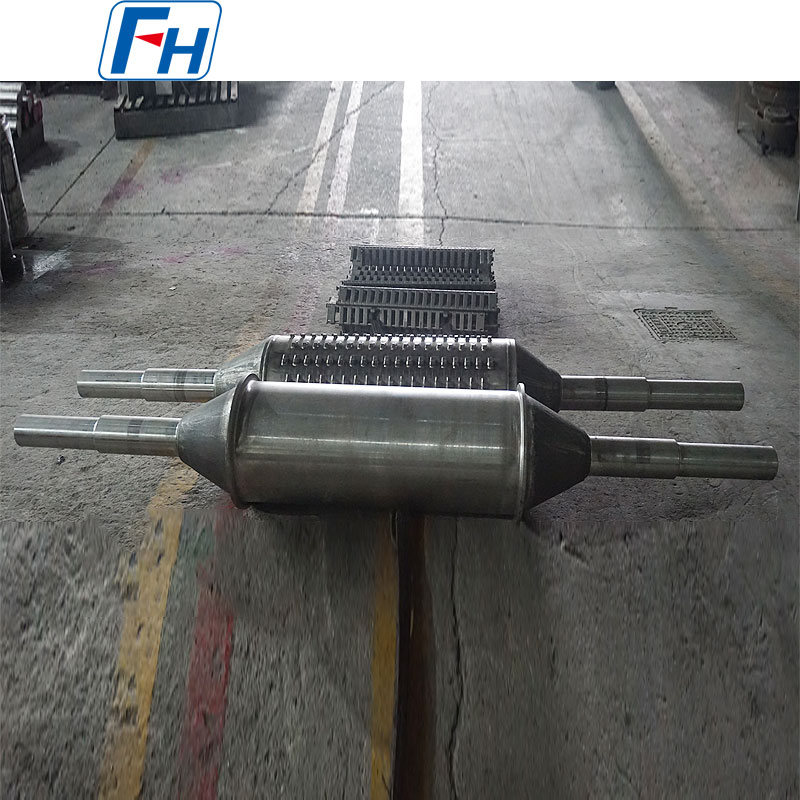
Combined Application of Cast Drive Roller and Cast Link Belt
The combination of cast drive roller and cast link belt is a common configuration in industrial conveying systems, especially suitable for harsh conveying scenarios with high temperature and heavy load. The detailed introduction is as follows:
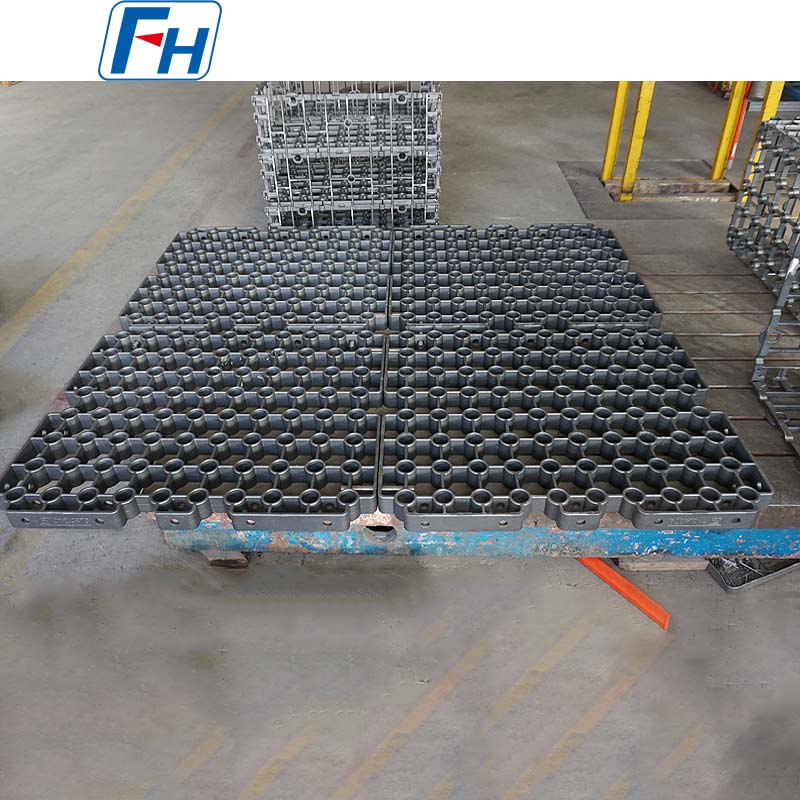
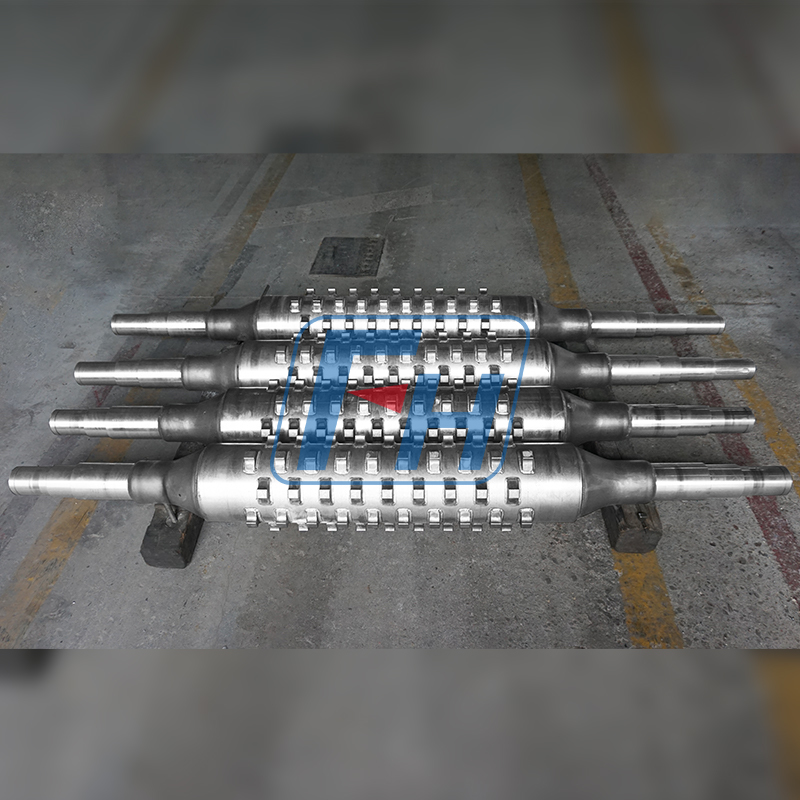
Cast Drive Roller
Structural Features:
Adopts an integrated casting-welding structure, with a circular locking device at the connection between the shaft and the hub to avoid stress concentration and transmit torque more efficiently and reliably. The main body of the roller is mostly formed by casting-welding, and can also be manufactured by processes such as integral steel plate welding; the surface is often processed into a rubber-covered structure with herringbone or diamond patterns to enhance friction with the cast link belt and prevent slipping.
Material Selection:
The core material is mainly cast steel, and heat-resistant stainless steel such as 1.4825 and 1.4865 is selected for some high-temperature working conditions. Cast steel has high strength and excellent wear resistance, which can meet the demand for high torque transmission under heavy-load conditions; heat-resistant stainless steel is suitable for high-temperature environments and extends service life.
Working PrincipleL:
Directly connected to power sources such as motors, the power source drives the cast drive roller to rotate. Through the friction between the roller surface and the cast link belt, the conveyor belt is driven to operate in a predetermined direction, thereby realizing continuous material conveying.
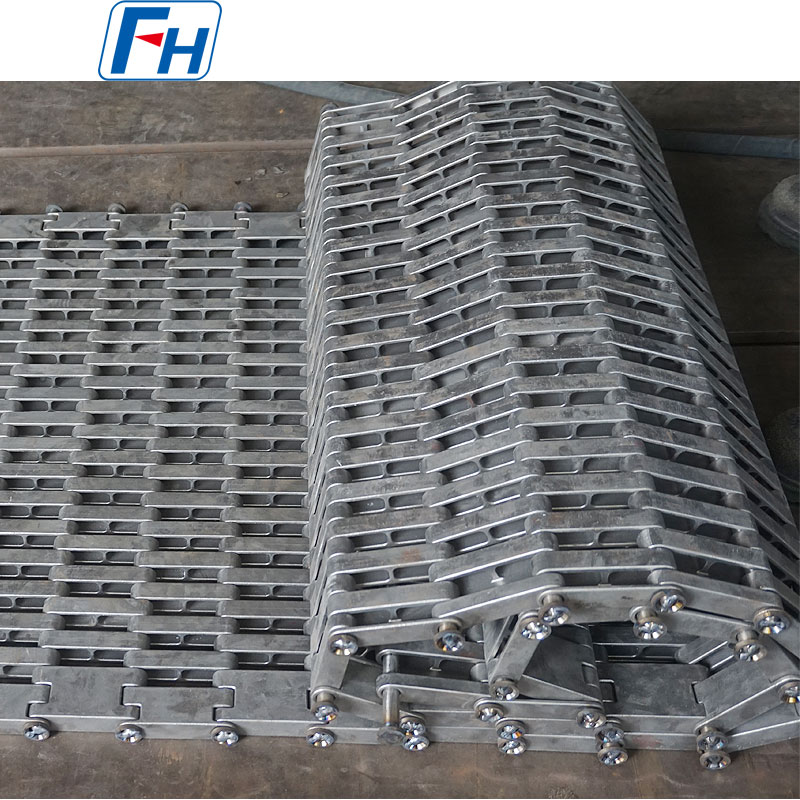
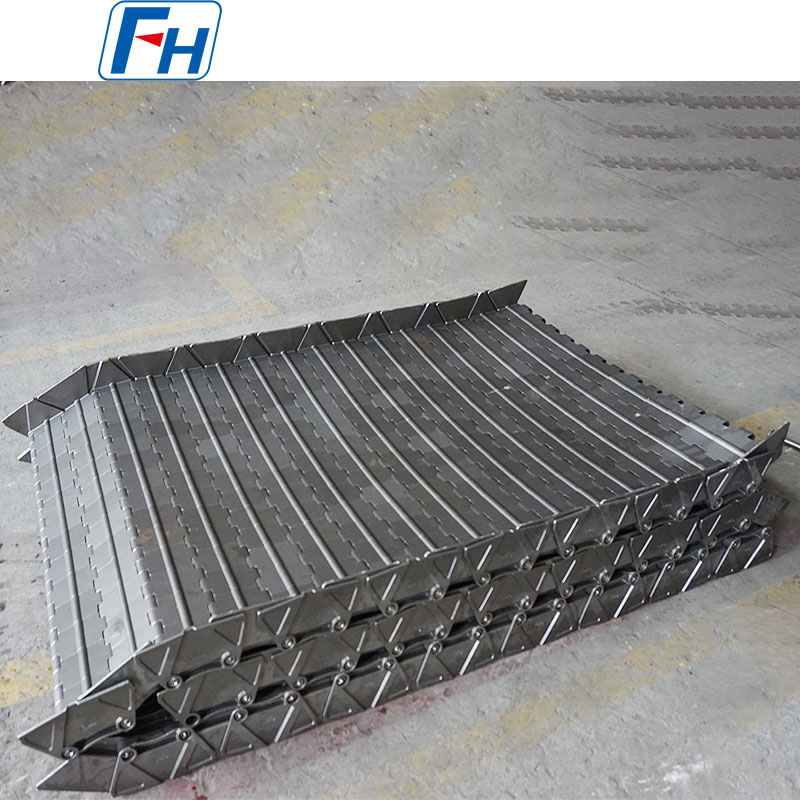
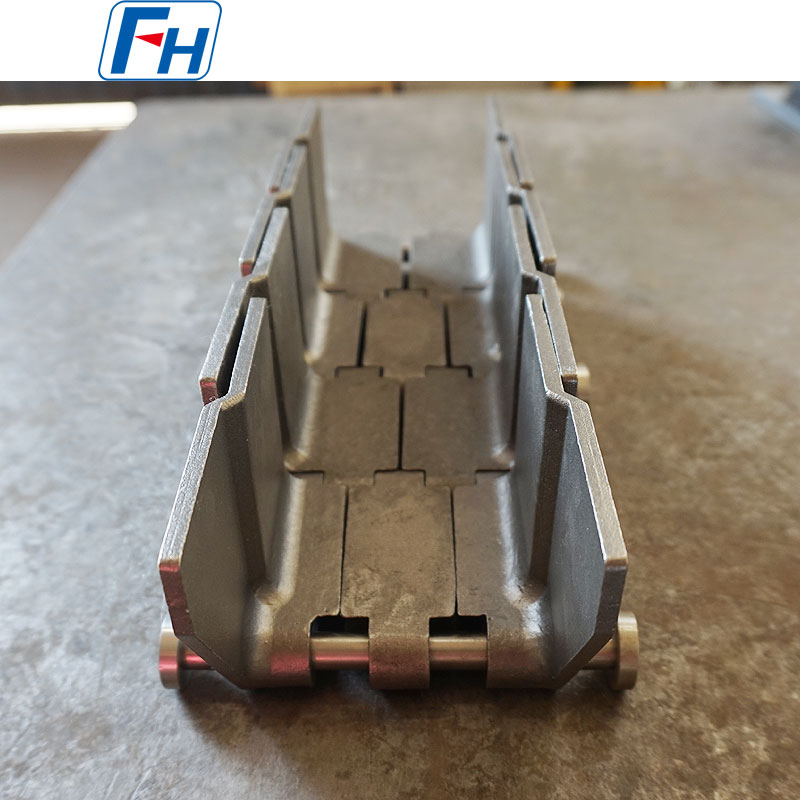
Cast Link Belt
Structural Features:
Composed of cast link plates and connecting pins, the link plates are connected row by row with short pins, and adjacent link plates in each row are further joined by small pins to form an integrated structure. Some models are equipped with rollers on the short pins, and the rollers are supported by parallel guide rails to further improve the stability of the conveyor belt operation and reduce friction loss.
Material Selection:
Common materials for link plates and pins include malleable cast iron, ductile iron, and heat-treated steel. Heat-resistant alloys such as 1.4848 and 1.4849 can be used for high-temperature and heavy-load scenarios. The material combination balances high load-bearing capacity, wear resistance and impact resistance to meet the needs of complex working conditions.
Working Principle:
Takes the cast drive roller as the power core, and realizes movement relying on the frictional driving force between the drive roller and the conveyor belt. During operation, the link plate assembly is auxiliary supported by guide rails or idler rollers to avoid deviation and shaking, ensuring the stability and continuity of material conveying.
Core Application Scenarios:
● Heat Treatment Furnaces: Used to convey workpieces in continuous heat treatment furnaces, which can withstand high-temperature environments, ensure stable transmission of workpieces during the heat treatment process, and not affect process accuracy.
● Metallurgical and Mining Industry: Conveys heavy-load materials such as ore and coal. With high load-bearing and wear-resistant characteristics, it is suitable for harsh working conditions with field environments, high dust and strong impact.
● Cement and Building Materials Industry: Conveys high-temperature materials such as cement clinker on cement production lines, which can withstand high-temperature baking and wear of materials, ensuring continuous operation of the production line.

| Heat-resistant Steel | |||||||||||||
| / | GB (中) | DIN (德) | ASTM (美) | JIS (日) | Chemical Composition (%) | Maximum Operation Temperature | |||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Nb/Cb | Mo | Other | ||||||
| 1 | ZG40Cr27Ni4 | 1.4823 | HD | SCH11 | 0.30 - 0.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤1.00 | 24.00 - 28.00 | 4.00 - 6.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 1050℃ |
| 2 | ZG40Cr22Ni10 | 1.4826 | HF | SCH12 | 0.30 - 0.50 | 1.00 - 2.50 | ≤2.00 | 19.00 - 23.00 | 8.00 - 12.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 950℃ |
| 3 | ZG30Cr28Ni10 | - | HE | SCH17 | 0.20 - 0.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 26.00 - 30.00 | 8.00 - 11.00 | - | - | - | 1050℃ |
| 4 | ZG40Cr25Ni12 | 1.4837 | HH | SCH13 | 0.30 - 0.50 | 1.00 - 2.50 | ≤2.00 | 24.00 - 27.00 | 11.00 - 14.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 1050℃ |
| 5 | ZG30Cr28Ni16 | - | HI | SCH18 | 0.20 - 0.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 26.00 - 30.00 | 14.00 - 18.00 | - | - | - | 1100℃ |
| 6 | ZG40Cr25Ni20Si2 | 1.4848 | HK | SCH21 | 0.30 - 0.50 | ≤1.75 | ≤1.50 | 23.00 - 27.00 | 19.00 - 22.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 1100℃ |
| 7 | ZG30Cr20Ni25 | - | HN | SCH19 | 0.20 - 0.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 19.00 - 23.00 | 23.00 - 27.00 | - | - | - | 1100℃ |
| 8 | ZG40Cr19Ni39 | 1.4865 | HU | SCH20 | 0.35 - 0.75 | ≤2.50 | ≤2.00 | 17.00 - 21.00 | 37.00 - 41.00 | - | - | - | 1020℃ |
| 9 | ZG40Cr15Ni35 | 1.4806 | HT | SCH15 | 0.35 - 0.70 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 15.00 - 19.00 | 33.00 - 37.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 1000℃ |
| 10 | ZG40Cr25Ni35Nb | 1.4852 | HPCb | SCH24Nb | 0.30 - 0.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 24.00 - 28.00 | 33.00 - 37.00 | 0.80 - 1.80 | ≤0.50 | - | 1100℃ |
| 11 | ZG40Cr19Ni39Nb | 1.4849 | - | - | 0.30 - 0.50 | 1.00 - 2.50 | ≤2.00 | 18.00 - 21.00 | 36.00 - 39.00 | 1.20- 1.80 | ≤0.50 | - | 1100℃ |
| 12 | ZG40Cr24Ni24Nb | 1.4855 | - | - | 0.30 - 0.50 | 1.00 - 2.50 | ≤2.00 | 23.00 - 25.00 | 23.00 - 25.00 | 0.80 - 1.80 | ≤0.50 | - | 1050℃ |
| 13 | ZG40Cr25Ni35 | 1.4857 | HP | SCH24 | 0.35 - 0.50 | 1.00 - 2.50 | ≤2.00 | 24.00 - 28.00 | 33.00 - 37.00 | - | ≤0.50 | - | 1100℃ |
| 14 | ZG1Cr20Ni32Nb | 1.4859 | - | - | 0.06 - 0.15 | 0.50 - 1.50 | ≤2.00 | 19.00 - 21.00 | 31.00 - 33.00 | 0.50 - 1.50 | ≤0.50 | - | 1050℃ |
| 15 | ZG45Cr12Ni60 | - | HW | - | 0.35 - 0.75 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 10.00 - 14.00 | 58.00 - 62.00 | - | - | - | 1100℃ |
| 16 | ZG45Cr18Ni66 | - | HX | - | 0.35 - 0.75 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | 15.00 - 19.00 | 64.00 - 68.00 | - | - | - | 1100℃ |
| 17 | ZG1Cr28Co50 | 2.4778 | - | - | 0.05 - 0.25 | 0.50 - 1.00 | ≤1.50 | 27.00 - 30.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.50 | Co:48.0 - 52.0 | 1200℃ |
| 18 | ZG30Cr28Co50Nb | 2.4779 | - | - | 0.25 - 0.35 | 0.50 - 1.50 | 0.50 - 1.50 | 27.00 - 29.00 | - | 1.50 - 2.50 | ≤0.50 | Co:48.0 - 52.0 | 1200℃ |
| 19 | ZG40Cr28Ni48W5 | 2.4879 | - | SCH42 | 0.35 - 0.55 | 1.00 - 2.00 | ≤1.50 | 27.00 - 30.00 | 47.00 - 50.00 | - | ≤0.50 | W:4.0 - 5.5 | 1200℃ |







Q: How to give inquiry ?
A: Step 1, please give us some details about your furnace,operating temperature,cooling method,loading weight of your furnace and so on;
Step 2, it's better to provide 3D drawings;
Step 3, when we have enough details, we may design the products drawings and quote accordingly;
Q: When can I get the price?
A: We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry(Except weekend and holidays). If you are very urgent to get the price, please email us or contact us in other ways so that we can offer you a quote.
Q: When will make delivery ? /What is the delivery Time?
A: -Sample Order: 35 days after receipt of the full payment.
-Stock Order: 10 days after receipt of the full payment
-OEM Order: 30 days after receipt of the deposit.
Q: What's your after-sales service?
A: 1 year warranty for all kinds of products;
If you find any defective accessories first time, we will give you the new parts for free to replace in the next order, as an experienced manufacturer, you can rest assured of the quality and after-sales service.
Q: What's your payment condition?
A: T/T
Payment<=USD10000, 100% in advance. Payment>USD10000, 50% T/T in advance ,balance before shipment.
Q: What is the shipping method?
A: Transported by DHL, UPS, EMS, Fedex,Air freight, sea freight or train freight.


 English
English Español
Español italiano
italiano Deutsch
Deutsch 0086-13338774804
0086-13338774804






















 Tel: 0086-510-88331288
Tel: 0086-510-88331288  E-mail:
E-mail:  Add: Room 1105,Building 6, Jiaye Wealth Center,Wuxi, Jiangsu, P.R.China P.C.:214000.
Add: Room 1105,Building 6, Jiaye Wealth Center,Wuxi, Jiangsu, P.R.China P.C.:214000. 