What are Heat Resistant Steel Castings?
1. Definition: Heat resistant steel castings are alloy steel castings that maintain their strength, toughness, and dimensional stability in high-temperature environments above 650°C. They belong to the heat-resistant alloy steel series and are often enriched with high levels of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to enhance their oxidation and corrosion resistance.
2. Main Alloy Composition: Typical formulations include 10–30% Cr, a small amount or no Ni, and appropriate amounts of Mo, C, and Mn. High chromium provides an oxide protective layer, Mo enhances high-temperature strength, and moderate carbon improves creep resistance.
3. Operating Temperature Range:
The design operating temperature is generally between 650°C and 1100°C, with some special alloys reaching 1200°C.
4. Key Performance Characteristics:
High-Temperature Strength and Creep Resistance: Maintaining sufficient yield strength under sustained high temperatures.
Oxidation Resistance: A dense Cr₂O₃/Al₂O₃ oxide film forms on the surface, preventing further oxidation.
Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion even in high-temperature oxidizing or corrosive environments.
How to evaluate the corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance of thermally resistive steel castings?
1. Laboratory Corrosion Testing
ASTM G48 Pitting/Crevice Corrosion Test: Determines the critical pitting temperature (CPT) to assess corrosion resistance in high-temperature chloride environments.
Intergranular Corrosion: Detects the depth of grain boundary corrosion using methods such as ASTM E112 to determine the effect of precipitation on relative corrosion.
2. High-Temperature Oxidation Experiment
Isochronous oxidation is performed in air or an oxidizing atmosphere at 800°C–1100°C. The oxide film thickness, mass increment, and oxidation rate are measured to determine the density of the oxide protective layer.
3. Microstructure and Phase Analysis
SEM/EDS, Optical Microscopy: Observe the distribution of σ phase, carbides, and precipitates; these secondary phases are sensitive sites for corrosion and oxidation.
XRD: Confirm the composition of the oxide film (Cr₂O₃, Al₂O₃, etc.).
4. Effects of Heat Treatment and Homogenization
Homogenization heat treatment (e.g., holding at 1150°C–1205°C for 1–4 hours) can significantly reduce precipitates and increase corrosion resistance.
Water quenching or slow cooling after melt annealing: Compare the effects of different cooling methods on oxide film density and select the optimal process.
In which industries and equipment are Wuxi Junteng Fanghu Alloy Casting Co., Ltd.'s heat-resistant steel castings mainly used?
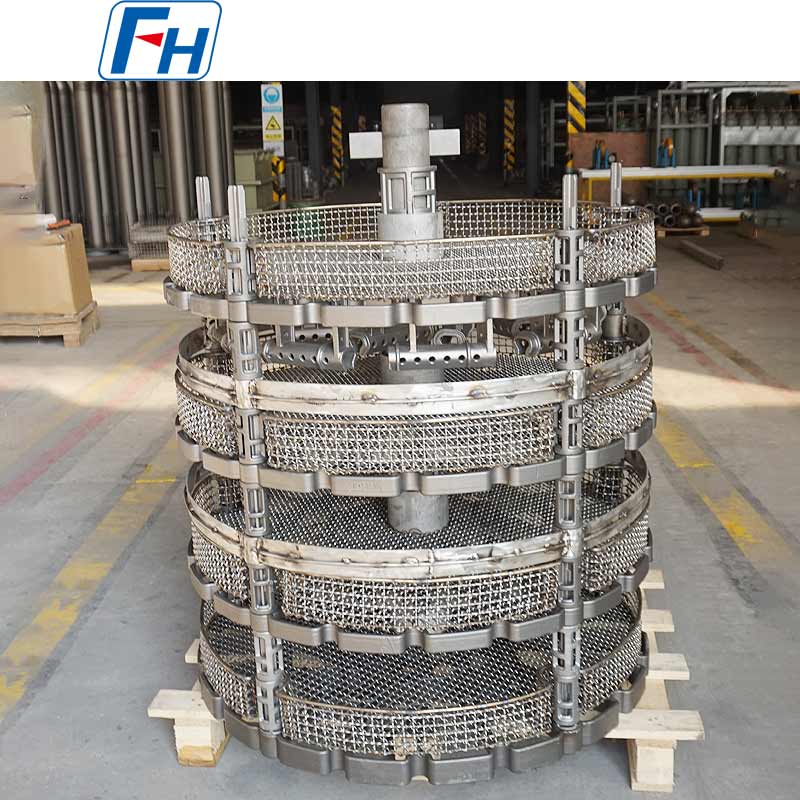
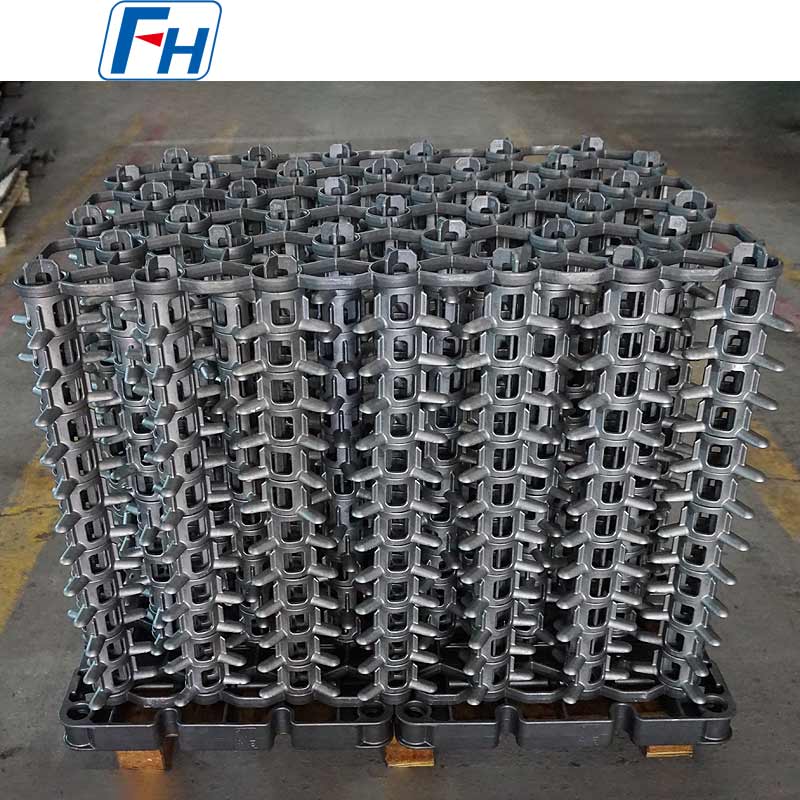
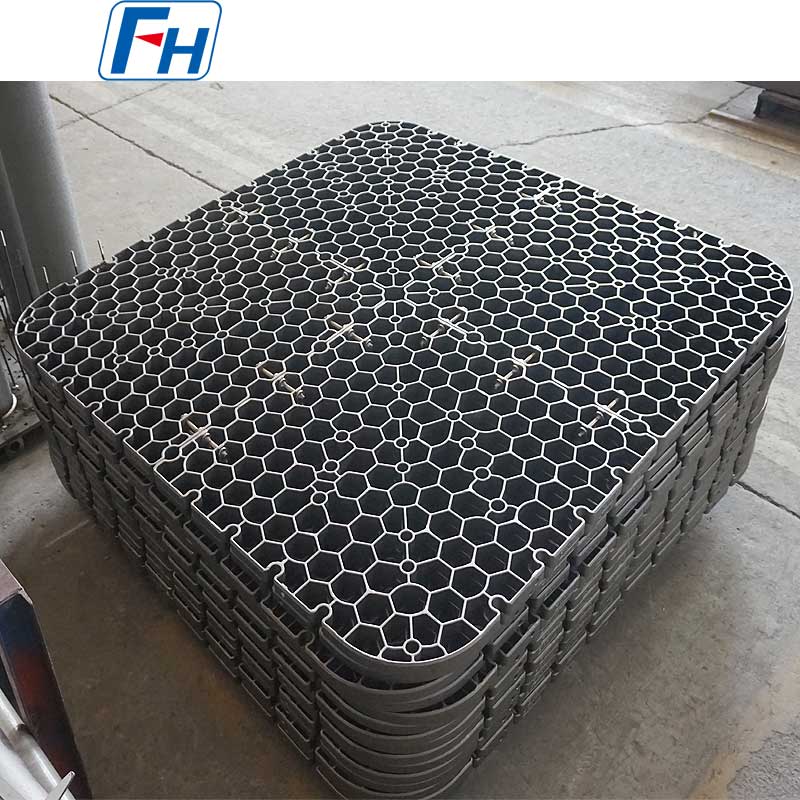
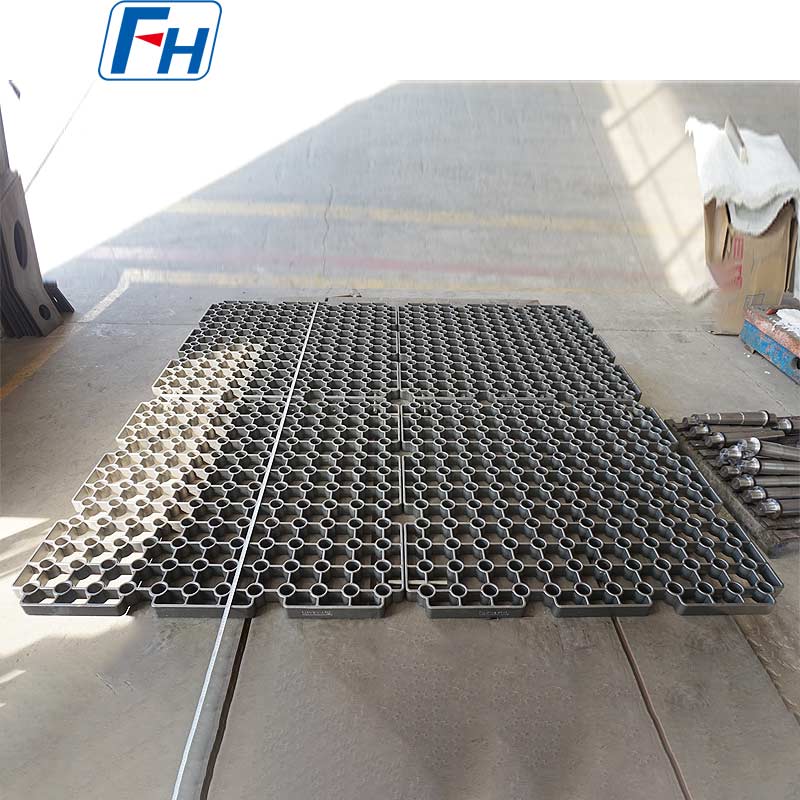
1. Heat Treatment Equipment
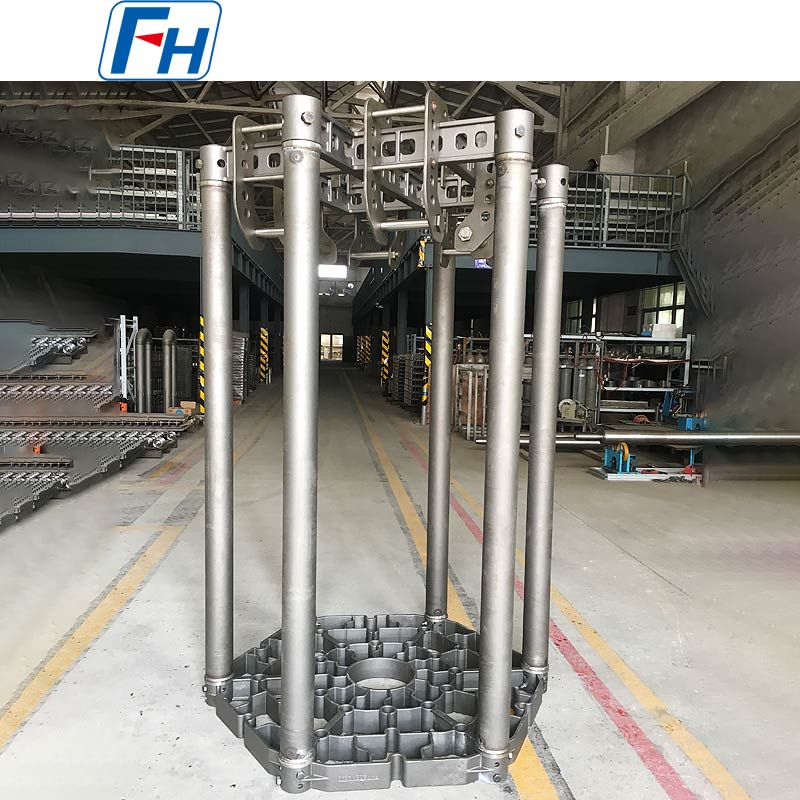
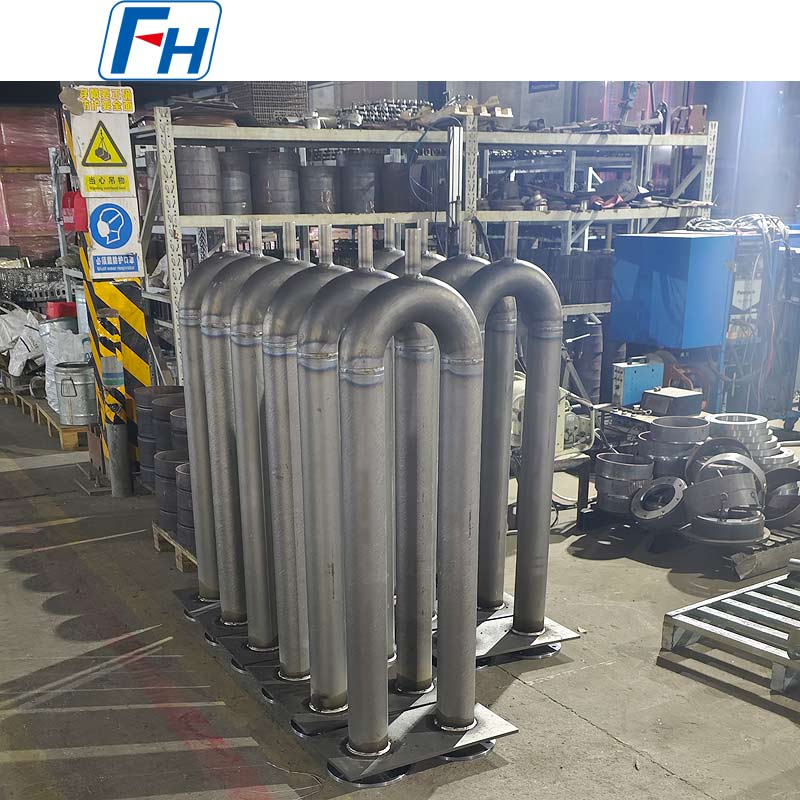
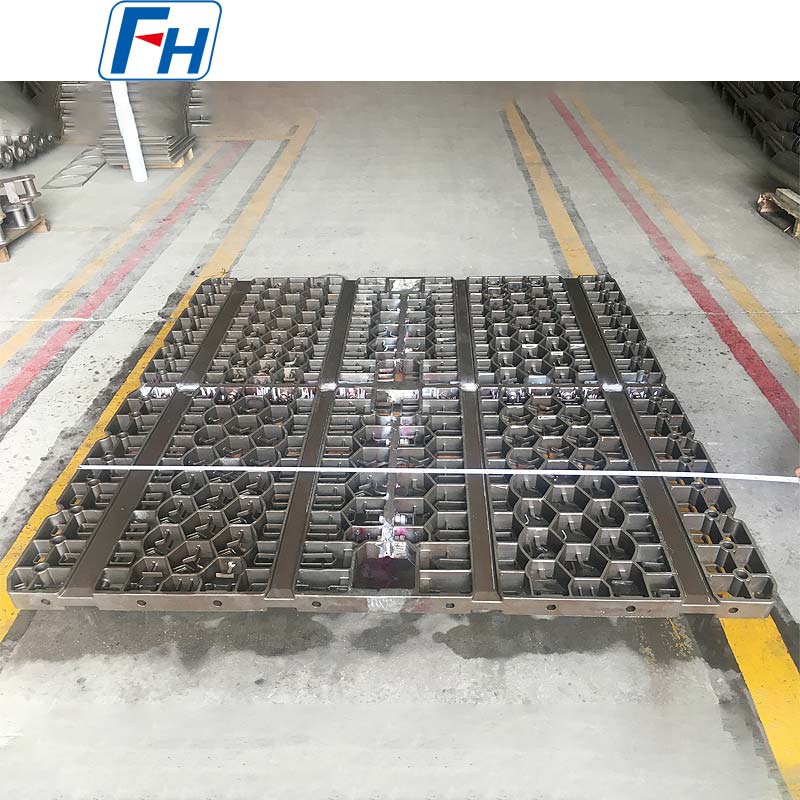
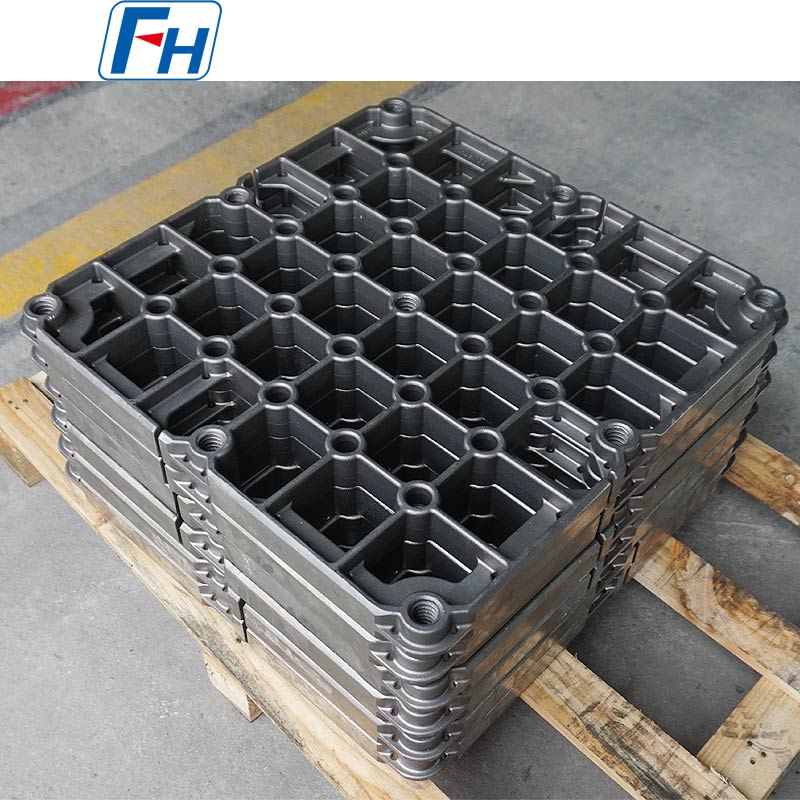
Key components such as heat treatment fixtures, radiant tubes, furnace rollers, fan blades, furnace rails, and wheels are widely used in metal heat treatment furnaces, carburizing, quenching, and other processes.
2. Metal Smelting and High-Temperature Processing: Internal structural and supporting components of heating furnaces, rotary furnaces, and smelting furnaces, subjected to high-temperature cycles and mechanical loads.
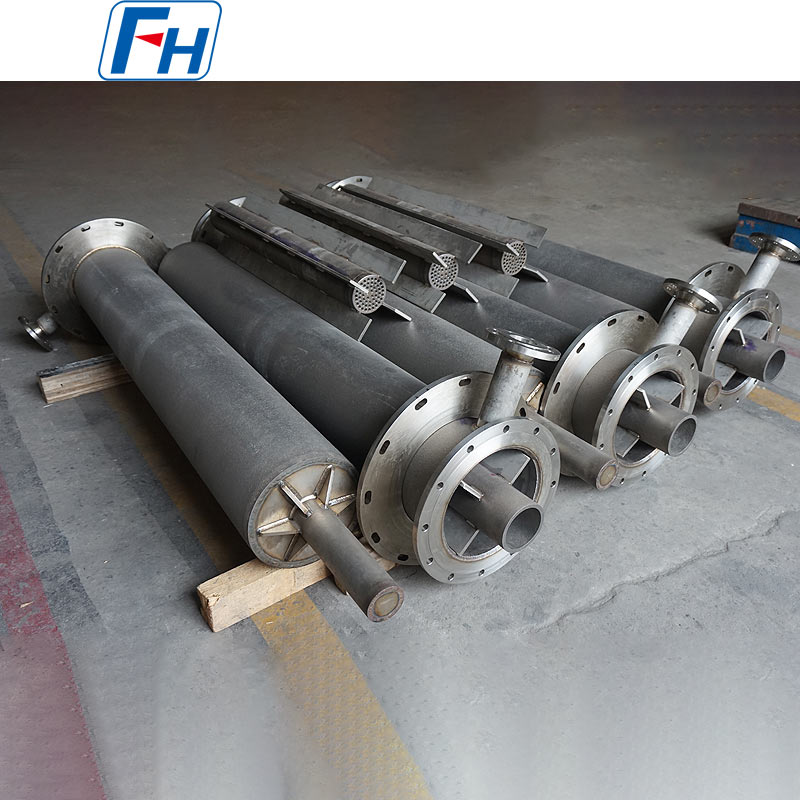
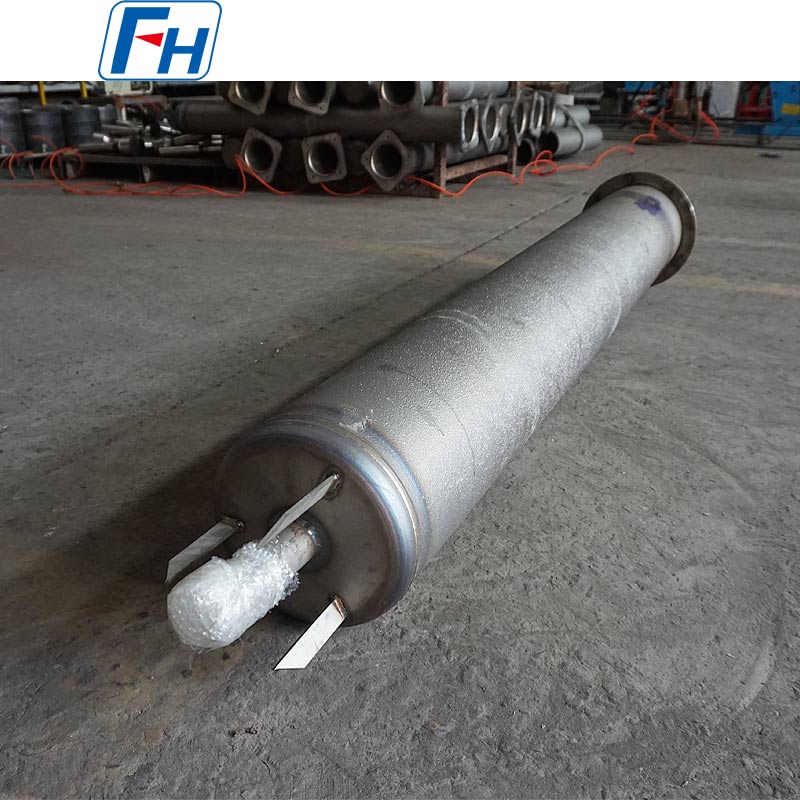
3. Petrochemical and Energy Industries: Key components requiring high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, such as high-temperature heat exchangers, combustion furnaces, and industrial kilns, improving equipment lifespan and operating efficiency.
4. Customization and Technical Services: The company provides OEM production, technical assistance, and material and dimension optimization to help customers achieve cost-effective heat treatment solutions.



 English
English Español
Español italiano
italiano Deutsch
Deutsch 0086-13338774804
0086-13338774804





























 Tel: 0510-83310100
Tel: 0510-83310100  E-mail:
E-mail:  Add: Room 1105,Building 6, Jiaye Wealth Center,Wuxi, Jiangsu, P.R.China P.C.:214000.
Add: Room 1105,Building 6, Jiaye Wealth Center,Wuxi, Jiangsu, P.R.China P.C.:214000. 